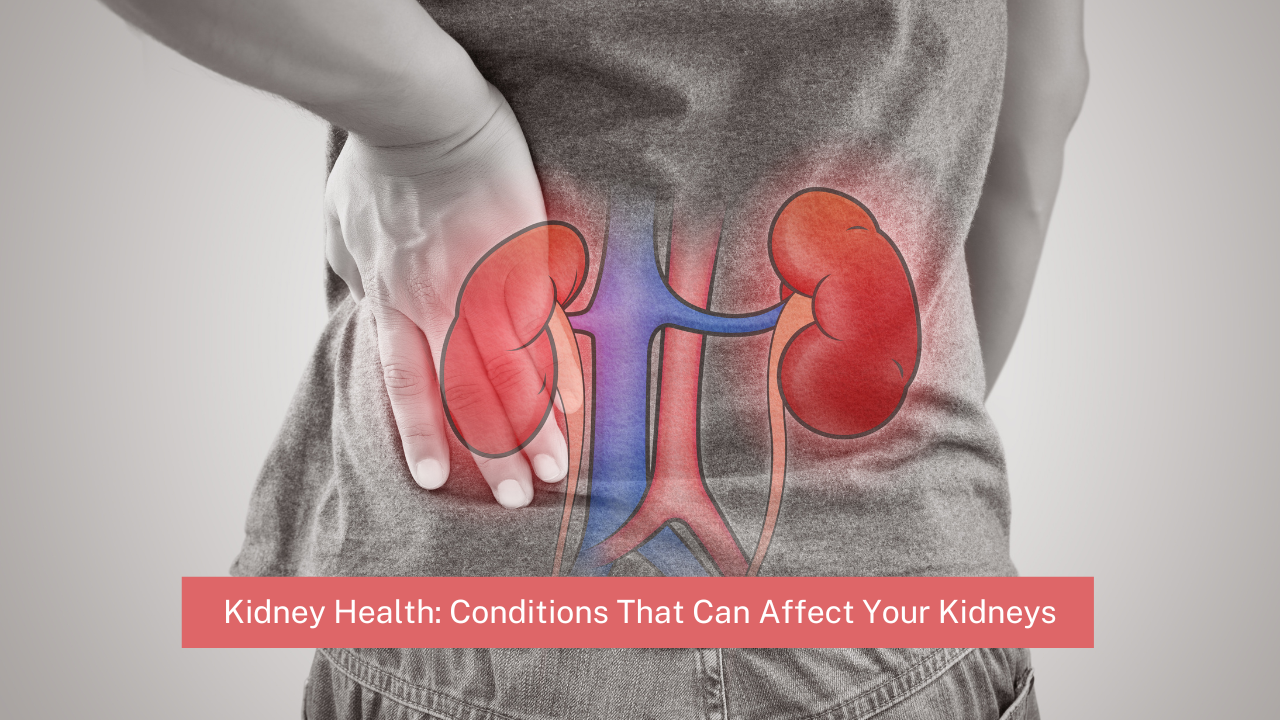
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, ureters (tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder), and urethra (tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body). Urinary Tract Infections are usually caused by bacteria, but they can also be caused by viruses or fungi.
Common symptoms of a urinary tract infection include:
1. Frequent and strong urge to urinate
2. Pain or a burning sensation during urination
3. Cloudy, bloody, or strong-smelling urine
4. Pain or pressure in the lower abdomen or back
5. Feeling tired or shaky
6. Fever or chills (a sign that the infection may have reached the kidneys)
If you suspect you have a Urinary Tract Infections, it is important to see a kidney specialist for proper diagnosis and treatment. They may ask for a urine sample to test for the presence of bacteria or other signs of infection. Treatment for Urinary Tract Infections typically involves a course of antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. Drinking plenty of water and urinating frequently can also help flush out the bacteria.
To prevent Urinary Tract Infections, it’s important to maintain good hygiene, such as wiping from front to back after using the toilet, and drinking plenty of water to promote regular urination.
It’s worth noting that if you are experiencing symptoms of a Urinary Tract Infections, it’s best to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
If you or a loved one are facing kidney health challenges, don’t hesitate to reach out to Kidney Care Hospital for exceptional care and support. Visit our website today to book your appointment!